Understanding the duration, extent, and movement of Great Lakes ice is important for the Great Lakes maritime industry, public safety, and the recreational economy. Lake Erie is ice-prone, with maximum cover surpassing 80% many winters.
Multiple times a day throughout winter, GLERL’s 3D ice model predicts ice thickness and concentration on the surface of Lake Erie. The output is available to the public, but the model is under development, meaning that modelers still have research to do to get it to better reflect reality.
As our scientists make adjustments to the model, they need to compare its output with actual conditions so they know that it’s getting more accurate. So, on January 13th of this year, they sent a plane with a photographer to fly the edge of the lake and take photos of the ice.
The map below shows the ice model output for that day, along with the plane’s flight path and the location of the 172 aerial photos that were captured.
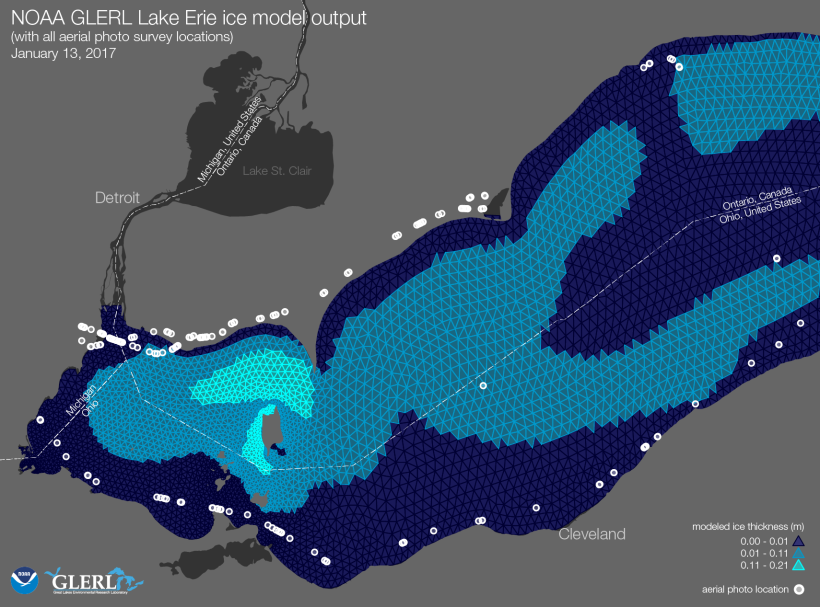
NOAA GLERL Lake Erie ice model output with all aerial photo survey locations — January 13, 2017. Map Credit NOAA GLERL/Kaye LaFond.
These photos provide a detailed look at the sometimes complex ice formations on the lake, and let our scientists know if there are places where the model is falling short.
Often, the model output can also be compared to images and surface temperature measurements taken from satellites. That information goes into the GLSEA product on our website (this is separate from the ice model). GLSEA is useful to check the ice model with. However, it’s important to get this extra information.
“These photographs not only enable us to visualize the ice field when satellite data is not available, but also allow us to recognize the spatial scale or limit below which the model has difficulty in simulating the ice structures.” says Eric Anderson, an oceanographer at GLERL and one of the modelers.
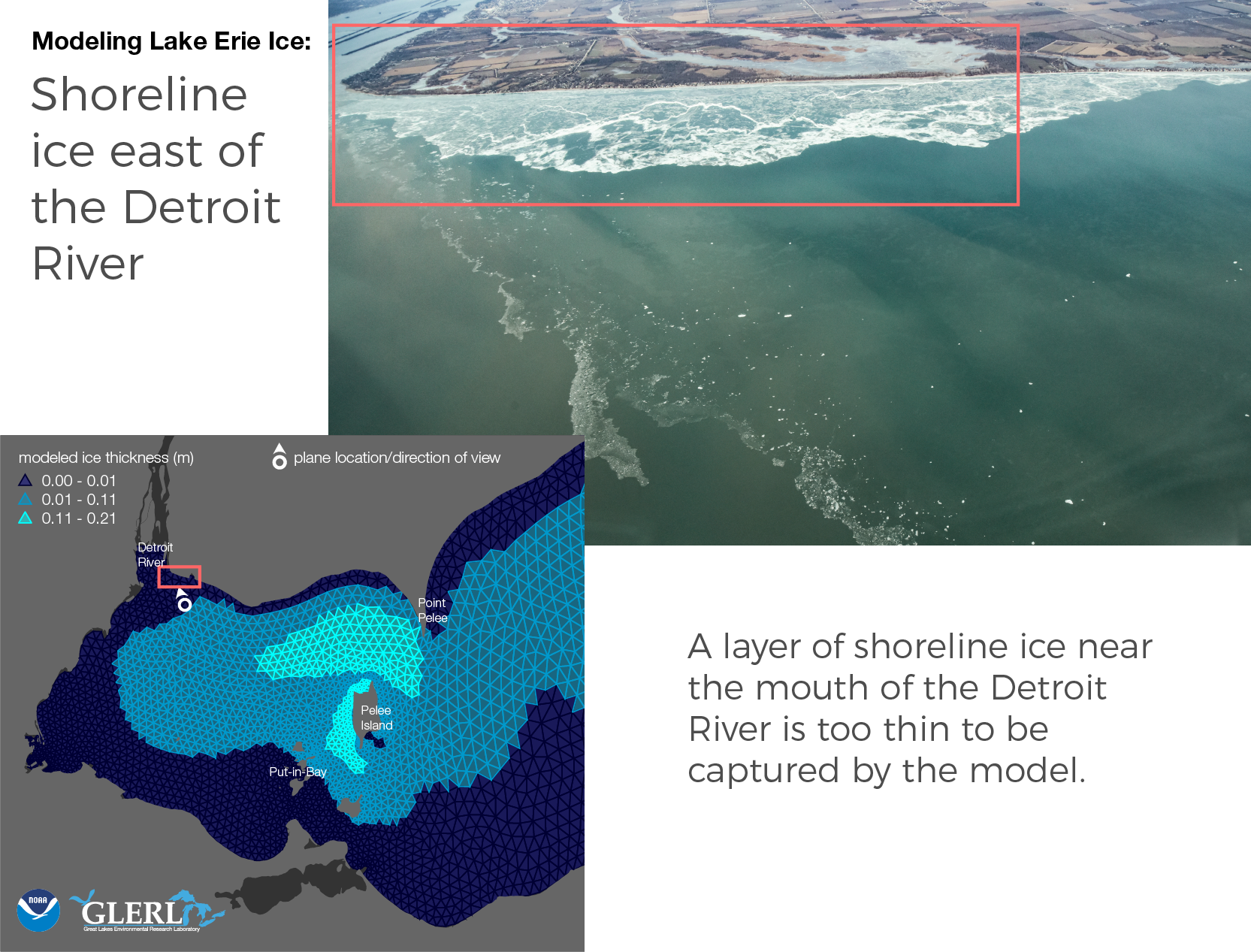
“This is particularly evident near the Canadian coastline just east of the Detroit River mouth, where shoreline ice and detached ice floes just beyond the shoreline are not captured by the model. These floes are not only often at a smaller spatial scale than the model grid, but also the fine scale mechanical processes that affect ice concentration and thickness in this region are not accurately represented by the model physics.”
Click through the images below to see how select photos compared to the model output. To see all 172 photos, check out our album on Flickr. The photos were taken by Zachary Haslick of Aerial Associates.
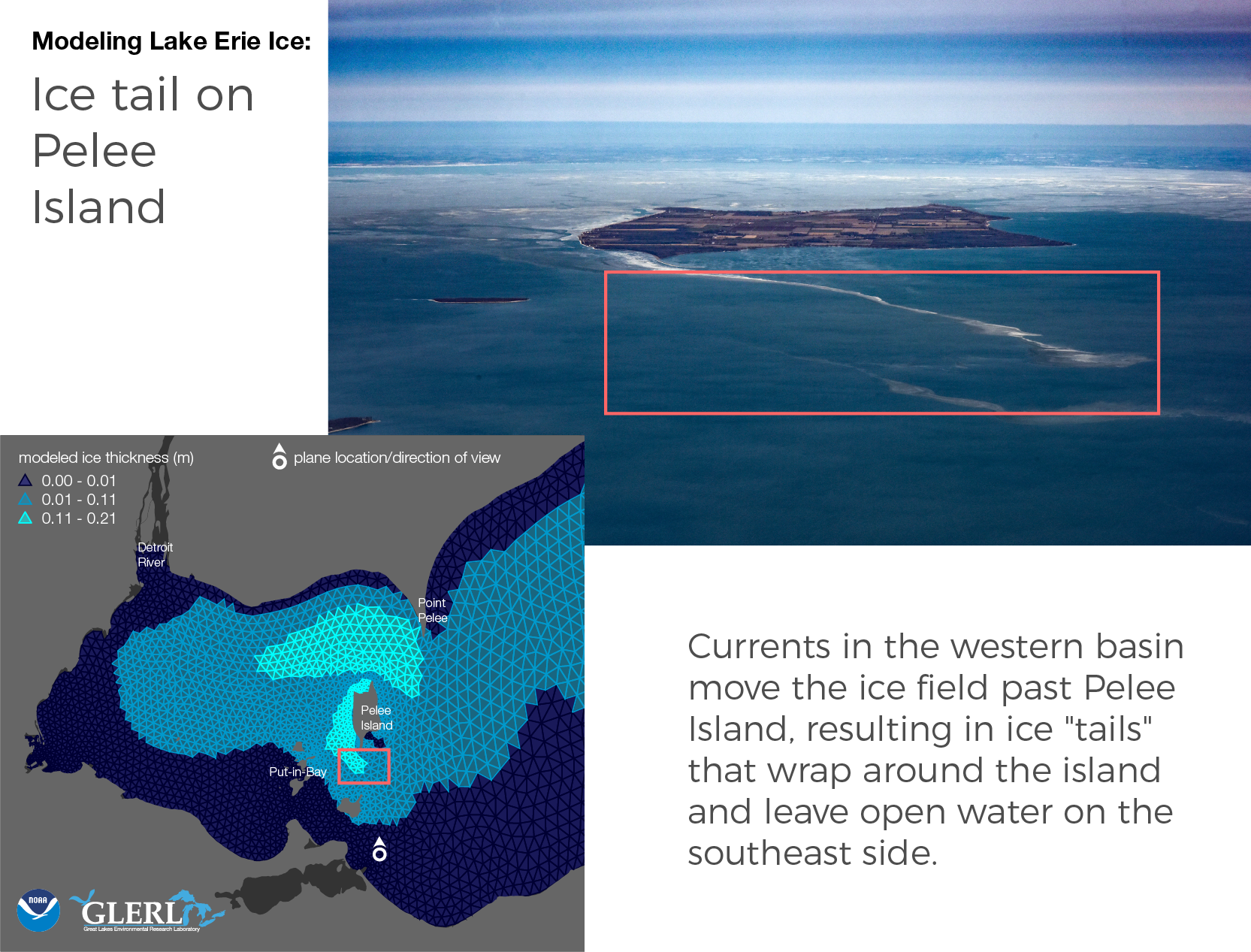
- Ice tail on Pelee Island. Photo Credit Zachary Haslick/Aerial Associates, Inc.
- Open water downstream of Pelee Island. Photo Credit Zachary Haslick/Aerial Associates, Inc.
- Ice edge northeast of Put-in-Bay. Photo Credit Zachary Haslick/Aerial Associates, Inc.
- Shoreline ice east of the Detroit River. Photo Credit Zachary Haslick/Aerial Associates, Inc.
- Shoreline and ice gap on the north shore. Photo Credit Zachary Haslick/Aerial Associates, Inc.
- Shoreline and ice gap on the north shore. Photo Credit Zachary Haslick/Aerial Associates, Inc.
- Ice field west of Point Pelee. Photo Credit Zachary Haslick/Aerial Associates, Inc.
- Ice field moving past Point Pelee. Photo Credit Zachary Haslick/Aerial Associates, Inc.







April 12, 2017 at 9:36 am
Fantastic article and fantastic science. Great job Kaye and Eric! And really wonderful photos!
LikeLiked by 1 person